Connecting Industrial IoT devices at the Edge

In this whitepaper by SUSE and Edgenesis, the spotlight is on the intricate challenges and inherent value for end customers in connecting Industrial IoT (IIoT) devices at the edge. This comprehensive document explores the hurdles such as scalability, security, and interoperability that industries face, and underscores the importance of a strategic approach in overcoming these obstacles. It offers an in-depth look into how Kubernetes can play a crucial role in not just addressing these challenges, but also in driving significant value for end customers by ensuring efficient, secure, and scalable IIoT deployments. This whitepaper is an essential read for stakeholders looking to navigate the complexities of IIoT implementations and unlock the full potential of edge computing.
Problem Definition
We’ll start with confronting the challenges at the heart of integrating IIoT devices at the network’s edge. We explore critical issues such as interoperability across diverse devices, the complexity of managing a large-scale device network, and the imperative for robust security measures to ward off cyber threats. Additionally, we touch on the difficulties of scaling these systems efficiently and the challenges of integrating them with legacy systems for real-time data processing. This section lays the groundwork for understanding the pressing needs in IIoT deployments, highlighting the importance of innovative solutions for a more secure and efficient industrial future.
Connecting IoT devices at the edge:
- Interoperability
- Industrial IoT devices often come from different manufacturers and may use various protocols, systems and data formats. This heterogeneity makes it difficult for these devices to communicate and work seamlessly together
- Management
- Managing a large number of IoT devices, each with different configuration, updates and monitoring needs is complex
- Complex onboarding processes can lead to extended deployment times, increased chances of errors, and higher initial setup costs
- Scaling
- As the number of connected devices grows, the system must be able to scale without a drop in performance. This includes handling increased data volumes and maintaining communication efficiency
- Security
- Each IoT devices could potentially be an entry point for cyber threats. Securing these devices, especially in a factory where they may not have been initially designed with strong security features is a significant challenge.
- Devices with outdated kernels or software are at risk of being exploited by cyber attacks, which could lead to data breaches or operational disruptions.
- Integration
- Integrating IoT devices with existing industrial systems (i.e. Legacy machines, ERP systems and more) and modern applications can be difficult due to differences in technology and standards.
- Architecture
- Designing an architecture that can handle the demands of IIoT in a factory setting, such as real-time data processing, low latency and high reliability is complex
- AI and the Future
- Technology, especially in the IoT domain, is evolving rapidly. Solutions implemented today must be adaptable and scalable to accommodate future technological advancements and changing industrial needs.
To address these challenges, solutions often involve the implementation of standardized protocols for interoperability, robust management and security systems, scalable architectures (like cloud or hybrid cloud environments), and integration platforms that can bridge the gap between different systems and technologies. The goal is to create a cohesive, secure, and efficient environment where IIoT devices can operate harmoniously and deliver the full range of their intended benefits.
Introducing Shifu
Shifu is a Kubernetes-native IoT platform. It extends Kubernetes’ into managing IoT devices as if they were native Kubernetes Pods. By virtualizing IoT devices into these Pods, Shifu encapsulates all the device-specific protocols and drivers into a containerized environment, enabling seamless management and deployment.
Shifu, Akri, Multus, RKE2 and SLE Micro integration
Multus: attaching multiple network interfaces to a pod
Akri: Device discovery (as an alternative to shifud)
Shifu: Deploy and manage connected deviceShifu inside Kubernetes cluster
SLE Micro: lightweight Linux OS at the edge
RKE2: Kubernetes runtime
Elemental: Edge onboarding and day 2 operations

Overall Architecture
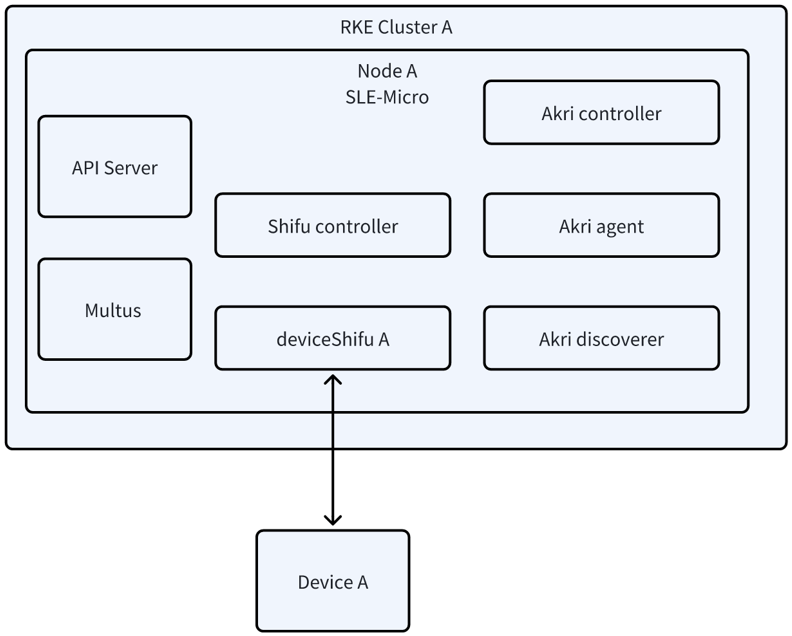
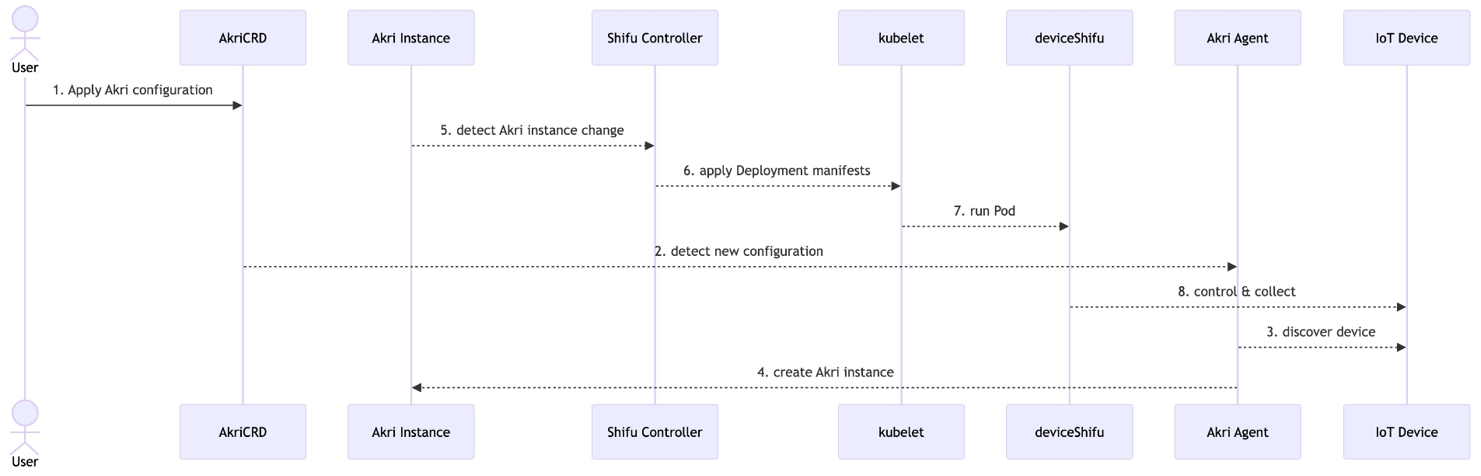
Shifu + Akri sequence
- Apply Akri configuration
- Broker
- Connection information
- Once Akri agent discovers the device, it creates an Akri instance
- Shifu controller detects Akri instance change, creates deviceShifu
- Listen to Akri event in Shifu Controller from Kube API server
- Deploys deviceShifu from Controller (Deployment, Service, EdgeDevice)
- Connection established
Detailed architecture
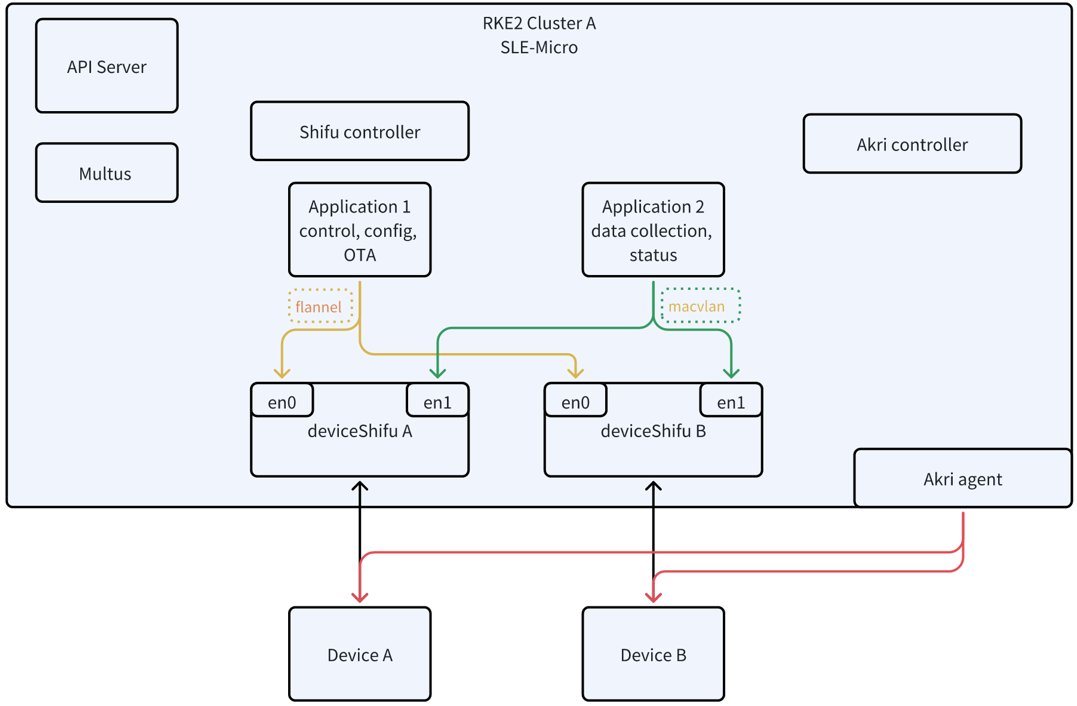
Day 2 Operation

Benefits of this integration
- Interoperability:
- Your use of Akri for device discovery allows for the identification of a wide range of devices using different protocols. Akri can be extended with various plugins to support new types of devices as they become available, promoting interoperability across heterogeneous devices.
- Shifu’s ability to deploy device/protocol pods ensures that each device can communicate with the cluster through a standardized interface, further enhancing interoperability.
- Management:
- The combination of Akri and Shifu provides a streamlined process for device management. Akri discovers devices and informs Shifu, which then manages the lifecycle of the corresponding deviceShifu pods.
- This automation reduces the management overhead and the risk of human error, while also providing a clear and simplified management interface through the Kubernetes API.
- Elemental streamlines the entire lifecycle of edge computing nodes, from initial deployment (Day 0) to ongoing management and updates (Day 2), using a centralized Kubernetes-native OS management system for seamless scalability and maintenance.
- Scaling:
- Kubernetes inherently supports scaling, and by integrating your IoT devices into the Kubernetes ecosystem using Shifu, you can leverage Kubernetes’ horizontal scaling capabilities.
- Multus allows you to attach multiple network interfaces to pods, which can help in scaling out your network architecture without being constrained by the limits of a single network interface.
- Security:
- The Kubernetes platform itself provides several built-in security features, such as role-based access control (RBAC), secrets management, and network policies, which can be utilized to secure your IoT infrastructure.
- Additionally, by encapsulating devices within pods, you can apply Kubernetes’ security best practices to each IoT device, thus standardizing and potentially improving the security posture across all devices.
- Elemental enhances the security of edge computing infrastructures by providing a minimal OS layer specifically tailored for Kubernetes, ensuring that nodes are equipped with just the essential components to reduce the attack surface and facilitate secure, automated updates.
- Integration:
- With deviceShifu, you can create custom resources in Kubernetes for each IoT device, which can then be managed and used like any other Kubernetes resource. This seamless integration into the Kubernetes ecosystem enables easier management and integration with other applications and services running in the cluster.
- SLE Micro as a Kubernetes runtime at the edge is optimized for lightweight and reliable operation, suitable for edge computing where resources might be limited.
- Architecture:
- This solution is built on a microservices architecture, which is inherently modular and resilient. Each component (Akri, Multus, Shifu) plays a specialized role and can be updated independently, ensuring a flexible and maintainable system.
- The use of edge computing through SLE Micro allows for decentralized processing, reducing latency and bandwidth use by processing data closer to the source.
- Need for AI and Future-Proofing:
- By integrating with Kubernetes and leveraging edge computing, you create an infrastructure that is well-suited for implementing AI and machine learning models directly at the edge, enabling real-time analytics and decision-making.
- The modular nature of this solution ensures that as your needs evolve or as new technologies emerge, you can adapt and extend your system with minimal disruption. The use of open-source components also helps in keeping up with the latest advancements and community support.
Case study
Summary
Edgenesis collaborated with a factory automation company managing around 100 different types of IoT devices. Previously, they struggled with the integration of these devices into their system due to a lack of infrastructure engineering expertise. By utilizing our proprietary solution, Shifu, we optimized their software infrastructure by abstracting the IoT connectivity layers, effectively decoupling their application from protocol and connectivity logistics. This partnership allowed the engineers to concentrate on automation application logic rather than infrastructure concerns. As a result, Edgenesis helped the company achieve a significant increase in efficiency:
- Transformed a device integration process that would have taken years into one requiring just one Full-Time Worker (FTW) for 2 months to complete, translating to a staggering increase in efficiency.
- Streamlined the development process and reduced time required, saving an estimated $1.2 million in labor and overhead costs over the initial projection. This enhancement not only accelerated development but also significantly cut costs and resources, marking a milestone in the company’s operational capabilities in the factory automation sector.
| Before | After |
| The monolithic software architecture led to a cumbersome development cycle of approximately 6 months for minor updates, with a vulnerability to a single point of failure. | Transitioning to a microservice architecture slashed the development cycle for minor updates to a mere 2 weeks, while also achieving high system availability and eliminating the single point of failure. |
| Each software update process spanned roughly 2 weeks, bogged down by manual testing, which resulted in extended release cycles and escalated costs. | The introduction of automated testing truncated the testing phase to just 2 days, accelerating the release cycle by 90% and substantially reducing costs. |
| Device management was disjointed and spread out across various platforms, necessitating the use of an average of 3 distinct systems to control and monitor the devices. | A centralized approach to device management was implemented, consolidating the control and monitoring functions into a single system and thus reducing complexity. |
| The system was limited to handling only up to 50 devices at once before experiencing performance issues, which was not conducive to larger-scale operations. | The system’s capacity expanded to manage up to 500 devices simultaneously without any dip in performance, marking a tenfold increase in scalability and robustness for more complex operations. |
Challenges
Tight coupling limited system scalability and adaptability.

- The device drivers and applications were tightly integrated, any update risked disrupting the entire ecosystem. Leading to a slow and laborious development cycle.
- With over hundreds of different types of devices, each requiring unique communication protocols like RS485, OPC UA, MQTT, and RTSP, making standardization a formidable challenge.
- The existing monolithic architecture lacked the necessary scalability, posing significant challenges when attempting to integrate new devices or scale up to meet increasing demands.
Edgenesis’ solution

- Infrastructure-Business Logic Decoupling: Shifu decouples IoT management from business logic, allowing more agile application development and easier maintenance.
- Enhanced Scalability: Able to scale to millions of devices. The new architecture was designed with scalability in mind, making it easier to add and integrate new devices into the system as the operational needs grow.
- Shorter Release Cycles: By standardizing device communication through protocol abstraction, Shifu minimizes the complexity involved in device integration. This streamlined process results in significantly shorter release cycles, enabling quicker deployment of updates and new features.
- Improved Security: With the ability to update the operating system and applications within a shorter release cycle, the solution effectively reduces the lifespan of any critical vulnerabilities (CVEs), thereby enhancing the system’s security and reliability over time.
- Centralized Management: The application at the core of the RKE2 Cluster communicates with the various ‘deviceShifu’ modules via HTTP, centralizing device management and allowing for streamlined monitoring and control from a single point.
Conclusion
The integration of Shifu, Akri, Multus, RKE2 and SLE Micro represents a significant leap forward in managing IIoT devices at the edge. This synergy offers a more flexible, scalable, and cost-efficient approach to edge computing. Such a transformative shift in IIoT device management underscores the critical need for IT professionals to adopt Kubernetes-native solutions, designed with precision for edge environments. This whitepaper emphasizes the importance of embracing these innovations to enhance operational efficiencies and drive future advancements in industrial IoT.
Contact SUSE and Edgenesis today to unlock the potential of your industrial processes and secure a technology foundation that’s built for the future. Embrace the opportunity to simplify the complexities of IIoT and safeguard your infrastructure with confidence. Let’s chart a course towards a smarter, more efficient, and protected IIoT ecosystem together.
Authors:
 Tom Qin, Co-Founder & Chief SRE at Edgenesis
Tom Qin, Co-Founder & Chief SRE at Edgenesis
Experienced software engineer with a proven track record at Veriflow Systems. Co-founder and Chief SRE at Edgenesis, designing Shifu (a Kubernetes-native IoT framework) and leading the engineering team. Passionate about technology and innovation.
 Andrew Gracey, Lead Product Manager for Cloud Native Edge at SUSE
Andrew Gracey, Lead Product Manager for Cloud Native Edge at SUSE
Passionate about making a positive impact on the world through technical and human process design. Andrew has 9+ years of experience in the tech industry serving in roles requiring fast-paced and creative design, a solid understanding of project’s fit in the market, and project management/expectation management skills.