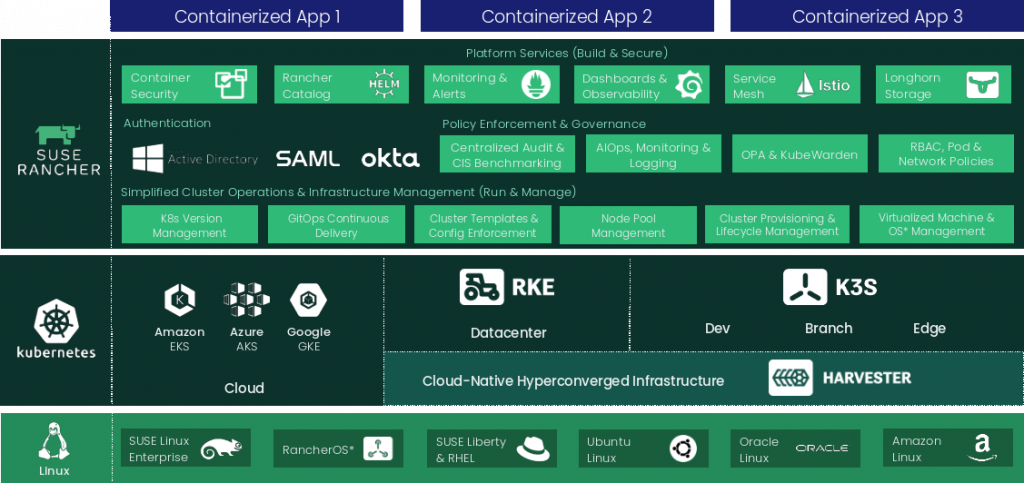
In the dynamic realm of IT infrastructure, Kubernetes has solidified its status as a pivotal force behind containerized environments, offering unparalleled capabilities in the deployment, management, and scaling of application containers across host clusters. As an influential open-source system, Kubernetes simplifies the complexities of managing containerized applications, promoting operational efficiency and resilience. This orchestration prowess has transformed operational paradigms, elevating the agility and scalability of applications to meet the demands of the modern digital landscape, thereby rendering Kubernetes an essential asset for businesses seeking competitive advantage.
Yet, the advantages of Kubernetes come with inherent security responsibilities. While beneficial for scalability and efficiency, the platform’s flexible and distributed architecture also presents a spectrum of security challenges. These challenges are increasingly exploited by adversaries aiming to infiltrate containerized applications and compromise sensitive data. In light of these challenges, prioritizing these new paradigms of security for Kubernetes deployments transcends traditional best practices—it becomes imperative. Adhering to Kubernetes-specific best practices is crucial for maintaining the security and integrity of applications and the data they handle. This article explores essential strategies for securing your Kubernetes environment, ensuring a robust defense against potential threats.
Understanding Kubernetes Security Risks
Kubernetes, while transformative in the world of container orchestration, introduces a complex security landscape that requires meticulous attention. This complexity is not just theoretical; it is reflected in the array of security challenges that can jeopardize Kubernetes environments. Among these challenges, several stand out due to their prevalence and potential impact.
Misconfigurations are perhaps the most ubiquitous security risk. The flexibility of Kubernetes often leads to complex configurations, and it’s alarmingly easy for administrators to inadvertently leave the door open to attackers. Whether it’s exposed dashboard interfaces, unnecessary privileges, or default settings left unchanged, such oversights can serve as entry points for malicious activities.
Vulnerabilities in container images and runtime represent another significant risk. Containers often rely on external images that may contain known vulnerabilities or be outdated. Without rigorous scanning and management, these vulnerabilities can be exploited by attackers to compromise the container and, potentially, the entire cluster.
Insufficient network policies can lead to unauthorized access and lateral movement within the cluster. Kubernetes’ default settings allow broad internal communication, which, if not correctly restricted by robust network policies, can enable attackers to exploit one vulnerable component to compromise others.
Lack of access controls is a critical issue. Kubernetes environments can be complex, with various roles requiring different levels of access. Without proper role-based access control (RBAC) configurations, there’s a risk of overprivileged accounts that, if compromised, can lead to significant breaches.
The impact of these security breaches on organizations can be profound. Beyond the immediate operational disruptions and potential data loss, the reputational damage can have long-lasting effects on customer trust and business viability. Regulatory implications may also arise, with breaches involving sensitive data leading to significant fines under laws like GDPR.
In summary, understanding and mitigating the security risks in Kubernetes environments is not just about protecting IT assets; it’s about safeguarding the organization’s reputation, customer trust, and regulatory compliance.
Core Principles of Kubernetes Security
To navigate the intricate security landscape of Kubernetes, adhering to core principles is essential. These foundational strategies are designed to bolster the security posture of Kubernetes deployments, ensuring the safeguarding of both the infrastructure and the applications running within.
Least Privilege Access
The principle of Least Privilege Access is paramount in Kubernetes security. This approach entails granting users, services, and applications the minimal level of access—or privileges—necessary for their function. By implementing Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) effectively, organizations can minimize the risk associated with overprivileged accounts, which, if compromised, could lead to extensive system breaches. Tailoring permissions closely to the needs of each entity significantly reduces the attack surface, making it a critical first line of defense.
Defense in Depth
Defense in Depth is a multi-layered se
curity strategy that ensures if one security control fails, others are in place to thwart an attack. In the context of Kubernetes, this might involve securing the container images, enforcing network policies to restrict traffic flow, and isolating workloads to prevent lateral movement by attackers. By layering security measures, organizations create a more resilient defense against both external and internal threats.
Regular Auditing and Monitoring
Continuous Regular Auditing and Monitoring form the backbone of an effective Kubernetes security strategy. Monitoring in real-time allows for the immediate detection of suspicious activities and anomalies, while regular audits of configurations and permissions help identify and rectify potential vulnerabilities before they can be exploited. Embracing Kubernetes monitoring best practices ensures that the infrastructure remains secure and compliant over time.
Implementing these core principles of Kubernetes security is not a one-time task but an ongoing commitment. As Kubernetes environments evolve, so too must the strategies used to secure them. By prioritizing least-privilege access, adopting a defense-in-depth approach, and committing to regular auditing and monitoring, organizations can significantly enhance the security of their Kubernetes deployments.
Best Practices for Kubernetes Security
Securing a Kubernetes environment requires a multifaceted approach, embracing practices that span from the individual node and pod level to the overarching cluster management. This section delves into a series of best practices designed to fortify Kubernetes deployments against the myriad of security threats they face.
Securing the Kubernetes API
- Role-Based Access Control (RBAC): RBAC is crucial for defining who can access the Kubernetes API and what actions they can perform. By applying the least privilege principle, administrators can minimize the risk associated with overly broad permissions.
- Authentication and Authorization Mechanisms: Ensuring robust authentication and authorization mechanisms for the Kubernetes API protects against unauthorized access. Integrating with existing identity providers can streamline this process, leveraging tokens, certificates, or external auth services.
Network Policies and Segmentation
- Implementing Namespace Strategies: Namespaces allow for the segmentation of resources within a Kubernetes cluster, providing a scope for allocating permissions and applying policies.
- Using Network Policies to Restrict Traffic: Network policies are vital for controlling the flow of traffic between pods and namespaces, preventing unauthorized access, and ensuring that pods communicate only as intended.
Node Security
- Keeping Kubernetes and Its Components Up to Date: Regular updates are essential for addressing security vulnerabilities in Kubernetes and its components. Staying current with the latest versions can protect against known exploits.
- Hardening Node Configurations: Nodes should be hardened according to industry standards and best practices, including disabling unnecessary services and applying security patches.
Workload and Pod Security
- Secure Container Images: Utilizing secure and trusted container images is the foundation of pod security. This includes using trusted base images and scanning images for vulnerabilities to prevent the introduction of security flaws into the environment.
- Managing Secrets Securely: Kubernetes Secrets should be used for managing sensitive data within the cluster. It’s important to encrypt these secrets both at rest and in transit to protect them from unauthorized access.
- Implementing Pod Security Policies: Pod security policies enable administrators to enforce rules on the pod level, such as restricting privileged access and limiting resource usage to prevent denial-of-service (DoS) attacks.
Monitoring and Auditing
- Logging and Monitoring Strategies: Effective logging and monitoring are critical for detecting and responding to security incidents. Collecting logs from Kubernetes components and employing tools for real-time monitoring can provide insights into suspicious activities.
- Auditing Cluster Activities: Configuring audit logs allows for a detailed record of actions performed within the cluster, aiding in forensic analysis and compliance monitoring.
- Using Third-Party Tools for Enhanced Auditing Capabilities: To augment Kubernetes’ native capabilities, third-party tools can offer advanced features for monitoring, alerting, and auditing, providing a comprehensive view of the cluster’s security posture.
By adhering to these best practices for Kubernetes security, organizations can create a robust defense against the diverse array of threats targeting containerized environments. From securing the API and implementing network policies to hardening nodes and securing workloads, each measure plays a critical role in protecting the Kubernetes ecosystem. Continuous monitoring and auditing further ensure that the incident response teams can react to incidents to safeguard the integrity, confidentiality, and availability of applications and data.
Advanced Kubernetes Security Techniques
As Kubernetes environments grow in complexity and scale, leveraging advanced security techniques becomes essential to protect against sophisticated threats. Among these advanced methods, the implementation of a service mesh represents a significant leap forward in securing containerized applications.
Service Mesh for Enhanced Security
A service mesh is a dedicated infrastructure layer that facilitates service-to-service communication in a secure, fast, and reliable manner. It operates at the application level, providing a comprehensive way to manage how different parts of an application share data with one another.
The core advantage of a service mesh lies in its ability to enforce policies and provide insights across all traffic. It ensures that communication between services is secure, authenticated, and authorized. This level of control and visibility is vital in a microservices architecture, where applications consist of many loosely coupled services.
Implementing Secure Communications with mTLS
Mutual TLS (mTLS) is a cornerstone security fea
ture of service meshes. It automatically encrypts data in transit, ensuring that both parties in a communication are authenticated and authorized to talk to each other. mTLS provides a much-needed security assurance for intra-cluster communications, protecting against eavesdropping, tampering, and forgery.
Integrating with External Security Tools and Platforms
Service meshes can seamlessly integrate with external security tools and platforms, extending their capabilities to include threat detection, intrusion prevention, and more. This integration allows for a unified security posture that covers not only the infrastructure but also the application layer, offering a holistic approach to Kubernetes security.
Adopting a service mesh enhances Kubernetes security by providing an additional layer of control and visibility over service-to-service communications. Its ability to implement mTLS and integrate with other security solutions transforms the way security is managed within containerized environments, paving the way for more secure and resilient applications.
Maintaining Kubernetes Security
In the dynamic and ever-evolving landscape of Kubernetes, maintaining a strong security posture is an ongoing challenge that requires constant vigilance and proactive measures. As the Kubernetes ecosystem continues to grow, so too does the sophistication of threats targeting it. This necessitates a disciplined approach to security maintenance, underpinned by several key practices.
- Regular Vulnerability Scanning and Patch Management: Continuous vulnerability scanning of container images, Kubernetes codebase, and its dependencies is critical. Identifying vulnerabilities early allows for timely patching or mitigation, significantly reducing the window of opportunity for attackers. Coupled with effective patch management processes, this ensures that security flaws are addressed before they can be exploited.
- Continuous Security Assessment and Improvement: Security is not a one-time effort but a continuous cycle of assessment, improvement, and reinforcement. Regular security assessments—ranging from penetration testing to configuration audits—help identify potential weaknesses and areas for enhancement, enabling organizations to stay ahead of emerging threats.
- Staying Updated with Kubernetes Security Advisories and Updates: Keeping abreast of the latest security advisories and updates from the Kubernetes community is essential. These advisories provide critical information on vulnerabilities, patches, and best practices for securing Kubernetes environments. By staying informed, organizations can take swift action to apply updates and harden their clusters against known threats.
By embracing these practices, organizations can ensure that their Kubernetes deployments remain secure against the backdrop of an ever-changing threat landscape. Regularly scanning for vulnerabilities, continuously assessing and improving security measures, and staying updated with the latest advisories are pivotal steps in maintaining the integrity and resilience of Kubernetes environments.
Final Thoughts
The journey through Kubernetes security best practices underscores the critical nature of safeguarding containerized environments in an era where digital threats are constantly evolving. This exploration has illuminated the multi-faceted approach required to protect Kubernetes deployments—from securing the API and implementing robust access controls to adopting advanced security techniques and maintaining vigilance with regular updates and assessments.
As Kubernetes continues to play a pivotal role in the infrastructure of modern applications, the importance of adhering to these security best practices cannot be overstated. To navigate these complexities and ensure your Kubernetes environments are secure and resilient, consider leveraging the expertise and solutions offered by SUSE Rancher. With a strong commitment to open-source innovation and comprehensive security, SUSE Rancher provides the tools and support necessary to protect your containerized applications against the evolving threat landscape.
Explore SUSE Rancher’s Kubernetes solutions today and take the next step in securing your containerized infrastructure.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
How can I prevent unauthorized access to my Kubernetes API?
Preventing unauthorized access to your Kubernetes API involves a combination of configuring Role-Based Access Control (RBAC), enabling API authentication mechanisms, and using network policies to restrict access. RBAC allows you to define who can access the Kubernetes API and what they can do with it. Ensuring that API authentication is robustly configured helps verify the identities of users and services, while network policies limit the traffic to and from resources within the cluster, providing an additional layer of security.
What is the best way to manage secrets in Kubernetes?
The best way to manage secrets in Kubernetes is by using Kubernetes Secrets for storing sensitive data, such as passwords, tokens, and keys. Best practices include limiting access to Secrets using RBAC, avoiding hard-coding secrets into application code, and using tools or add-ons to encrypt Secrets at rest and in transit. Additionally, regularly rotating secrets and auditing access to them can significantly enhance security.
How can I ensure my container images are secure?
Ensuring container images are secure involves using trusted base images from reputable sources, scanning images for vulnerabilities regularly, and keeping images up-to-date to avoid security issues. Automated tools can help identify known vulnerabilities in container images, allowing you to address potential security issues before deploying them into production.
What are pod security policies, and why are they important?
Pod security policies are a Kubernetes feature that allows you to control the security specifications pods must comply with to run in your cluster. They are important because they limit the actions that pods can perform, reducing the risk of malicious behavior. Implementing pod security policies helps enforce best practices, such as preventing pods from running as root, limiting access to host filesystems, and restricting the use of privileged containers.
How do I monitor my Kubernetes environment for security threats?
Monitoring your Kubernetes environment for security threats involves implementing logging and monitoring strategies that provide visibility into your cluster’s operations. Collecting and analyzing logs from Kubernetes components, coupled with the use of tools for real-time monitoring and alerting, can help identify suspicious activities. This proactive approach allows you to detect and respond to security incidents promptly.
Can network policies enhance the security of my Kubernetes cluster?
Yes, network policies can significantly enhance the security of your Kubernetes cluster. They play a crucial role in implementing a zero-trust network model by segmenting traffic between pods and namespaces, effectively limiting who can communicate with whom. This segmentation helps prevent unauthorized access and lateral movement within the cluster, offering a robust mechanism to enforce your security policies at the network level.